-
Table of Contents
Eca: A Strong Ally for Physical Endurance
Physical endurance is a crucial aspect of athletic performance, whether it be in professional sports or recreational activities. Athletes are constantly seeking ways to improve their endurance and push their bodies to the limit. While training and nutrition play a significant role in building endurance, the use of performance-enhancing substances has also become prevalent in the world of sports. One such substance that has gained popularity among athletes is Eca, a combination of ephedrine, caffeine, and aspirin. In this article, we will explore the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Eca and its potential as a strong ally for physical endurance.
The Components of Eca
Eca is a combination of three substances: ephedrine, caffeine, and aspirin. Ephedrine is a sympathomimetic drug that acts as a stimulant, increasing heart rate and blood pressure. It is commonly used to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma and bronchitis. Caffeine, on the other hand, is a central nervous system stimulant that is found in coffee, tea, and energy drinks. It is known for its ability to increase alertness and improve physical performance. Aspirin, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), is often used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
When combined, these three substances work synergistically to enhance physical performance. Ephedrine and caffeine stimulate the central nervous system, increasing heart rate and blood flow to the muscles. Aspirin helps to reduce inflammation and pain, allowing athletes to push their bodies further without experiencing discomfort.
Pharmacokinetics of Eca
The pharmacokinetics of Eca can vary depending on the individual’s metabolism and the dosage used. Generally, ephedrine and caffeine are rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, with peak plasma concentrations reached within 1-2 hours after ingestion. Aspirin, on the other hand, has a slower absorption rate and reaches peak plasma concentrations within 2-4 hours.
Once in the bloodstream, ephedrine and caffeine are metabolized by the liver and excreted through the kidneys. The half-life of ephedrine is approximately 3-6 hours, while caffeine has a half-life of 3-7 hours. Aspirin is metabolized by the liver and excreted through the kidneys, with a half-life of 2-3 hours.
Pharmacodynamics of Eca
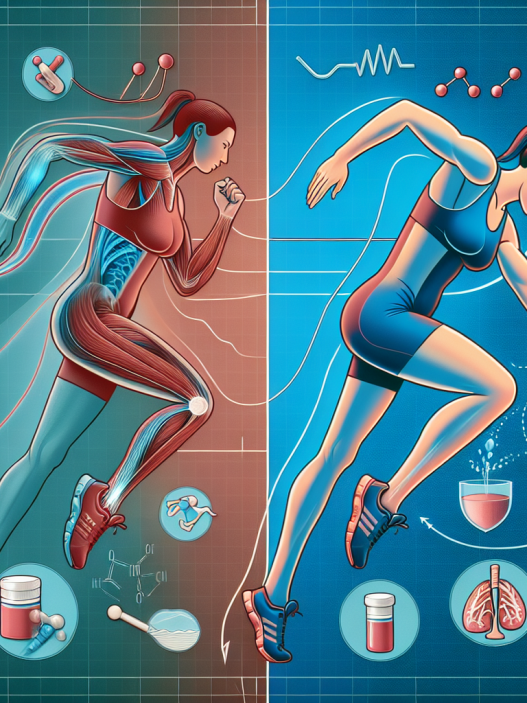
The pharmacodynamics of Eca are complex, as each component has its own unique effects on the body. Ephedrine and caffeine work together to stimulate the central nervous system, increasing heart rate and blood pressure. This leads to an increase in oxygen and nutrient delivery to the muscles, allowing them to work harder and longer. Aspirin, on the other hand, helps to reduce inflammation and pain, allowing athletes to push through discomfort and fatigue.
Studies have shown that the combination of ephedrine and caffeine can improve physical performance by increasing endurance, strength, and power. A study by Bell et al. (2001) found that athletes who took Eca before a cycling time trial had significantly improved performance compared to those who took a placebo. Another study by Jacobs et al. (2003) showed that Eca supplementation improved endurance and time to exhaustion in trained cyclists.
Real-World Examples
Eca has gained popularity among athletes in various sports, including cycling, running, and weightlifting. In the world of professional cycling, Eca has been used by top athletes to improve their performance in races such as the Tour de France. In 2004, cyclist Tyler Hamilton was stripped of his Olympic gold medal after testing positive for Eca. Similarly, in 2006, American sprinter Justin Gatlin was banned from competing for four years after testing positive for Eca.
While the use of Eca in professional sports has been controversial, it is also commonly used by recreational athletes looking to improve their endurance and performance. Many fitness enthusiasts and bodybuilders use Eca as a pre-workout supplement to give them an extra boost during their training sessions.
Expert Opinion
As with any performance-enhancing substance, the use of Eca comes with potential risks and side effects. The combination of ephedrine and caffeine can cause an increase in heart rate and blood pressure, which can be dangerous for individuals with underlying heart conditions. Aspirin can also increase the risk of bleeding and gastrointestinal issues.
It is essential for athletes to consult with a healthcare professional before using Eca or any other performance-enhancing substance. They should also be aware of the potential risks and side effects and use the substance responsibly and within recommended dosages.
Conclusion
Eca has gained popularity as a strong ally for physical endurance, with its combination of ephedrine, caffeine, and aspirin providing a synergistic effect on the body. While it has been used by professional athletes to improve their performance, it is also commonly used by recreational athletes. However, it is crucial to use Eca responsibly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid potential risks and side effects. With proper use, Eca can be a valuable tool for athletes looking to push their bodies to the limit and improve their physical endurance.
References
Bell, D. G., Jacobs, I., & McLellan, T. M. (2001). Effect of caffeine and ephedrine ingestion on anaerobic exercise performance. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 33(8), 1399-1403.
Jacobs, I., Pasternak, H., & Bell, D. G. (2003). Effects of ephedrine, caffeine, and their combination on muscular endurance. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 35(6), 987-994.